ii- Specific heat capacity of a substance (c in Jg-1 oC-1)
iii- Temperature change (θ in oC)
b) As chemical reaction occurs in an aqueous solution, assumptions are made during the calculation of heat of reaction :
Density of aq solution = Density of water = 1 g cm-3
Density of aq solution = Density of water = 1 g cm-3
Example :
- 1 cm3 of aq solution has a mass of 1 g
- 2 cm3 of aq solution has a mass of 2g
Energy change, H = mcθ
1) Heat of precipitation - Heat of precipitation is heat change when 1 mole of precipitate is formed from its ions.


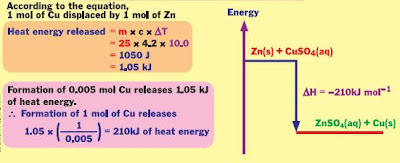
2) Heat of displacement- Heat of displacement is heat change when 1 mole of metal is displaced from its ionic solution by a more electropositive metal.

3) Heat of neutralisation - Heat of neutralization is heat energy released when 1 mole of water is formed from neutralization between one mole of hydrogen ions,H+ from an acid and one mole of hydroxide ions,


4) Heat of combustion- Heat of combustion is heat energy released (given off) when 1 mole of fuel is burnt completely in excess oxygen.


Comments
Post a Comment